What Is Sales Management? Skills, Roles, and Best Practices
May 24, 2022Hangover Cures: Effective Home Remedies Supported by Science
December 20, 2022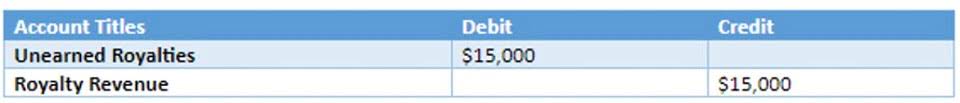
This action increased the number of shares outstanding, making the stock more accessible to a broader range of investors without affecting the company’s overall market capitalization. The issuance of stock dividends impacts the financial statements by increasing the number of outstanding shares while reducing retained earnings. Stock dividends can signal a company’s confidence in its future profitability, as they provide shareholders with additional shares without reducing the company’s cash reserves. Stock splits and stock dividends are corporate actions taken by a company to adjust its share structure without affecting the overall value of the company.
- The most common types of stock dividends are small stock dividends and large stock dividends.
- A) Lower the trading price of the stock per share.B) Increase the number of authorized shares.C) Increase legal capital.D) Increase the number of outstanding shares.
- This action requires adjustments in the equity section of the balance sheet but does not change the total equity value.
- This transaction requires adjusting the par value of the shares and updating the equity section of the balance sheet without affecting the total equity.
- Stock dividends also signal the company’s positive financial health and its ability to generate sufficient profits to support such distributions.
Large stock dividends and stock splits are issued primarily to:

On the other hand, stock dividends distribute additional shares to existing shareholders, which can affect retained earnings and paid-in capital. Unlike stock splits, stock dividends increase the number of shares and impact the company’s retained earnings, reflecting a distribution of profits to shareholders. Stock dividends have distinct financial statement effects compared to cash dividends. When a company issues a stock dividend, it distributes additional shares to existing shareholders proportionally. This does not impact the total value of shareholders’ equity but reallocates a portion of retained earnings to the common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts. Stock dividends, on the other hand, distribute additional shares to shareholders based on the number of shares they already own, typically expressed as a percentage.

How did Apple’s 7-for-1 stock split affect its total stockholders’ equity?
- Companies issue them to conserve cash, reward shareholders, and signal confidence in future earnings.
- Understanding their accounting treatments and effects on financial statements is crucial for investors and financial analysts.
- For instance, while a stock split might make shares more affordable and attractive to investors, it doesn’t change the underlying fundamentals of the company.
- From an accounting perspective, stock splits do not affect the total value of shareholders’ equity; instead, they merely increase the number of shares outstanding.
If you own 100 shares pre-split, you would receive a total of $100 as a quarterly dividend payment, the same as you would continue to receive after the split. This is because the total amount of dividends paid doesn’t change, even though the dividend per share is reduced. The dividend yield, which is calculated by dividing the annual dividend payment by the stock’s current price, can fluctuate significantly over time due to changes in the stock price. Stock splits don’t generate immediate income for shareholders, and they’re generally not considered taxable at the time of the split.
Accounting in the Headlines
A stock split is usually expressed as a ratio, such as 2-for-1 or 3-for-1, which means that each existing share is divided into two or three new shares. For example, if a company declares a 2-for-1 stock split, a shareholder owning 100 shares would receive large stock dividends and stock splits are issued primarily to: an additional 100 shares. For example, a 2-for-1 stock split would increase the number of shares from 100 to 200, while keeping the total market value the same.

Financial statements will reflect the increased number of shares outstanding, which may influence per-share metrics such as earnings per share (EPS). From an accounting perspective, stock splits do not impact the company’s balance sheet in terms of total equity. The primary effect is on the number of shares outstanding and the par value per share, which is reduced proportionally to the split ratio. As a result, the overall equity section https://www.bookstime.com/articles/freshbooks remains unchanged, reflecting the same total equity before and after the split. The issuance of stock dividends results in an increase in the number of shares outstanding. However, since the overall equity value remains unchanged, the per-share market price typically decreases to reflect the increased share count.
The split did not impact the company’s valuation but provided greater liquidity and trading flexibility for shareholders. However, neither stock splits nor stock dividends affect the company’s net income or cash flows directly. Corporations usually account for stock dividends by transferring a sum from retained earnings to permanent paid-in capital. The amount transferred for stock dividends depends on the size of the stock dividend. For stock dividends, most states permit corporations to debit Retained Earnings or any paid-in capital accounts other What is bookkeeping than those representing legal capital. In most circumstances, however, they debit Retained Earnings when a stock dividend is declared.